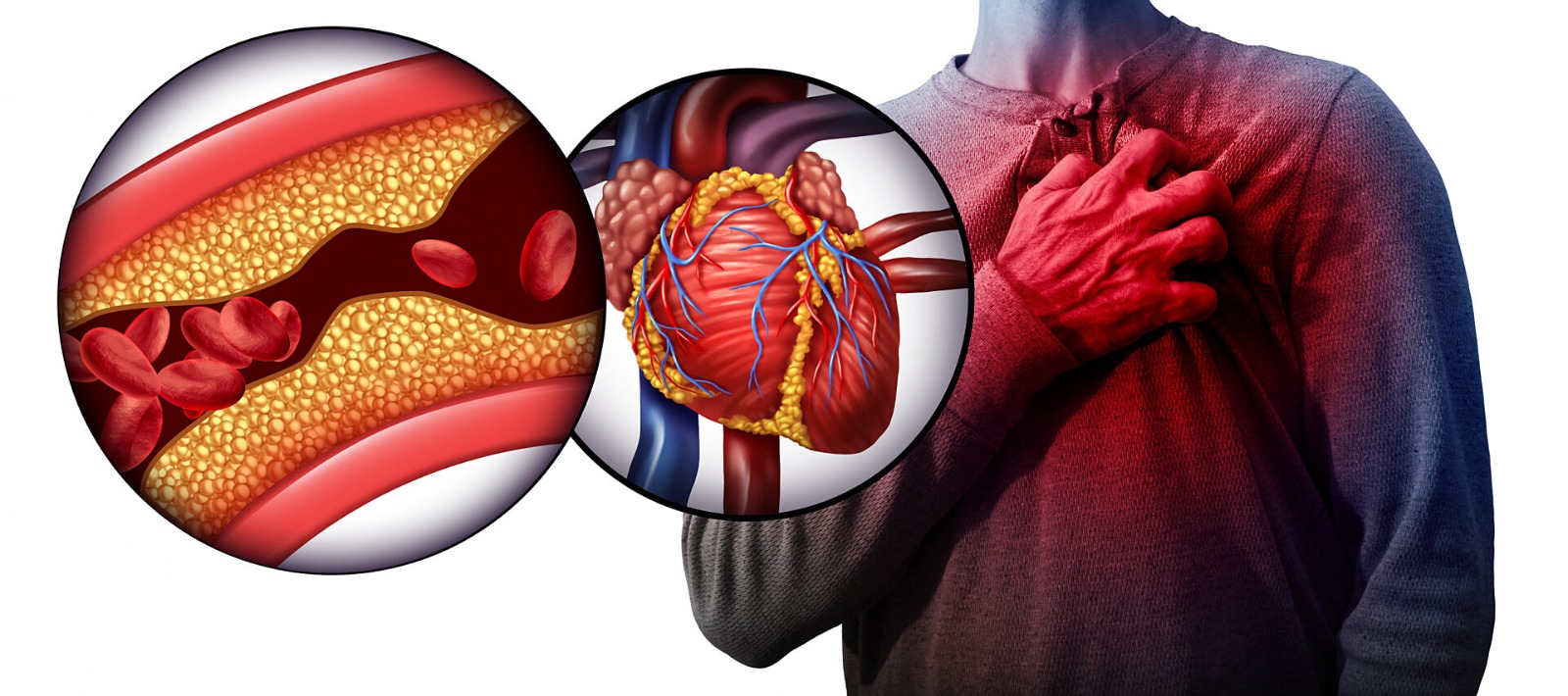
Which is more serious a heart attack or a cardiac arrest?
Are cardiac arrest and heart attack the same or different? The number of deaths caused by heart attacks is growing. The disease, which formerly used to affect adults, is now affecting the young generation. Stress is said to be the main reason for heart attacks, though change in lifestyle and dietary habits also contributes to the cause. This is why small children become victims of heart attack while at the gym, dancing or doing any other activity, which is sometime termed as cardiac arrest.
But what many people get confused is that two terms are similar. Heart attack, sometimes referred to as cardiac arrest, is it the same or different? Find out.
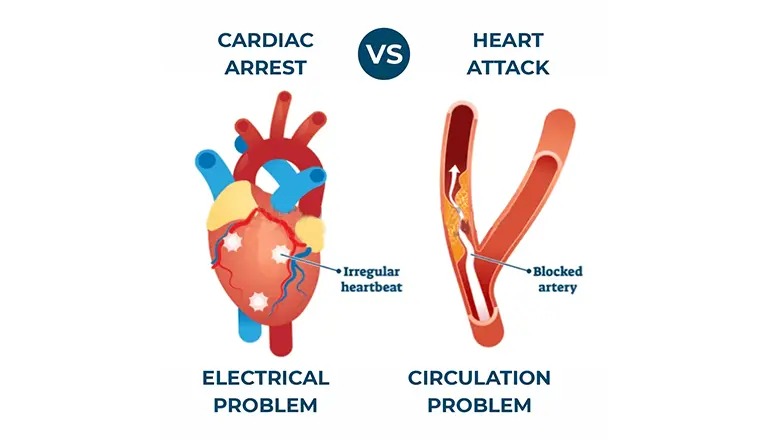
What is the definition of a heart attack and cardiac arrest?
These two are widely different. Differences are extreme between them. A heart attack happens when blood stops reaching the heart. The artery’s blood flow has halted, meaning oxygen supply has ceased to that body part. Hence, damage or dysfunction has been caused due to that particular portion which cannot get blood access.
This leads to death. This dangerous process takes time. However, cardiac arrest is sudden and without warning. When a person suffers cardiac arrest, their heart suddenly stops beating and they become permanently blind.
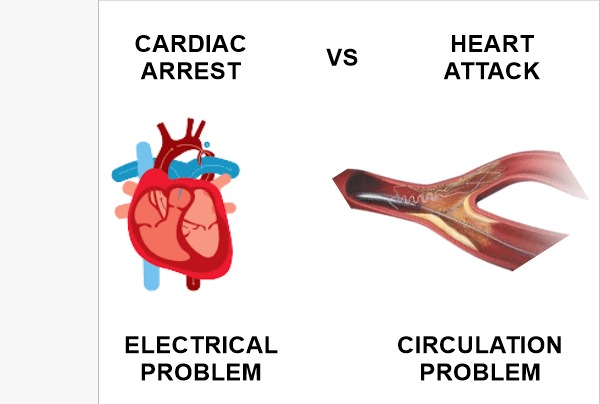
It has no symptoms and always manifests itself suddenly.
Most of the times we see people collapse and that is just due to cardiac arrest.
In cardiac arrest, suddenly the heart rate of a patient increases drastically and, he is unable to take proper breaths.
Blood pressure also stops.
Which one is more dangerous?
If we have to choose between the two, cardiac arrest is a more dangerous option. Because there are no symptoms. However, with cardiac arrest, there is no way to treat the patient.
Survival ways for cardiac arrest.
- Not to gain weight, the person has to do at least one hour physical activity per day.
- Carry out aerobic exercises including cycling, jogging, or any cricket, badminton, and football.
- Abstain from junk foods as much as possible
- Eat fruits and grains.
- High-fiber veggies, proteins, and legumes
- Avoid eating on full stomach or on an empty stomach for long.
- Get enough sleep. Do not stay up late or sleep too late in the morning.
- Avoid mobile phones and television as much as possible.
- Try to avoid stress and loneliness.
ALSO CHECK: What Is Heart attack: preventing heart disease